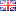
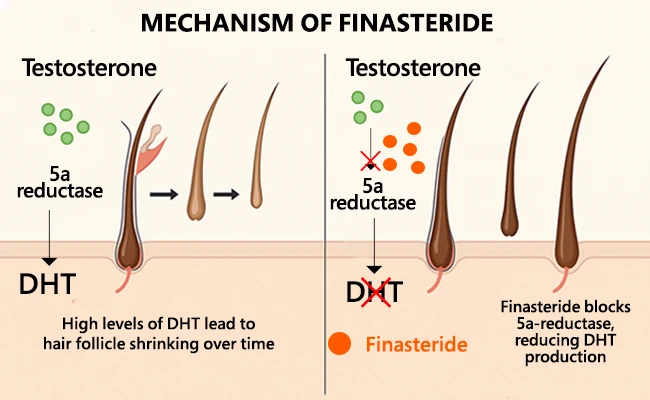
Finasteride is a pharmaceutical substance that belongs to type II 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, an enzyme that converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) — a more potent androgenic form of this hormone. DHT plays a key role in the development of androgenetic alopecia, as it is responsible for the gradual atrophy of hair follicles through the process of miniaturization.
Finasteride for Hair
Finasteride is one of the most effective pharmaceutical treatments for combating hair loss. Its efficacy is supported by numerous clinical studies and it has been approved by the relevant regulatory authorities (such as the FDA) for reducing hair loss and promoting hair regrowth.
In recent years, finasteride has been available in both systemic form (tablets) and topical form (solution or lotion), aiming either at generalized or targeted action on the scalp. Thanks to its high effectiveness and the ability to choose between topical and systemic therapy, finasteride is considered a cornerstone treatment in the management of male hair loss.
The selection of the appropriate form of administration depends on each patient’s medical history and individual needs. It is one of the few scientifically documented treatments that slow the progression of androgenetic alopecia and enhance hair density.


Finasteride is one of the most effective pharmaceutical treatments for combating hair loss. Its efficacy is supported by numerous clinical studies and it has been approved by the relevant regulatory authorities (such as the FDA) for reducing hair loss and promoting hair regrowth.
In recent years, finasteride has been available in both systemic form (tablets) and topical form (solution or lotion), aiming either at generalized or targeted action on the scalp. Thanks to its high effectiveness and the ability to choose between topical and systemic therapy, finasteride is considered a cornerstone treatment in the management of male hair loss.
The selection of the appropriate form of administration depends on each patient’s medical history and individual needs. It is one of the few scientifically documented treatments that slow the progression of androgenetic alopecia and enhance hair density.
What is finasteride
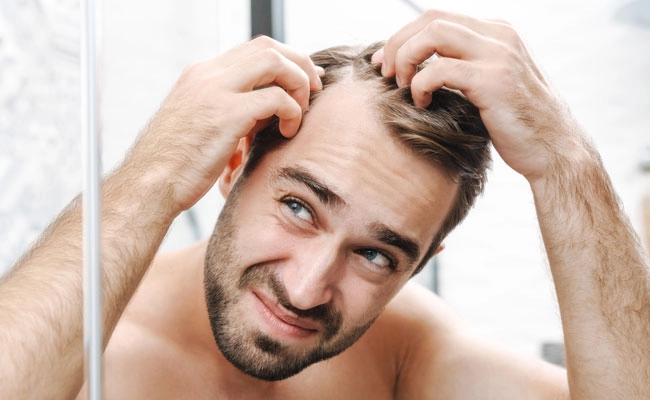
Mechanism of action of finasteride
Finasteride acts by inhibiting the specific enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, significantly reducing the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) — by up to 60–70% in the scalp. In this way, the hormonal effect on hair follicles is limited, resulting in a slowdown of hair loss and, in many cases, an enhancement of hair regrowth. Its action is gradual and requires daily use for at least 3 to 6 months before the first results become visible, while maximum improvement is usually achieved within one year.
What is finasteride

Mechanism of action of finasteride
Finasteride acts by inhibiting the specific enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, significantly reducing the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) — by up to 60–70% in the scalp. In this way, the hormonal effect on hair follicles is limited, resulting in a slowdown of hair loss and, in many cases, an enhancement of hair regrowth. Its action is gradual and requires daily use for at least 3 to 6 months before the first results become visible, while maximum improvement is usually achieved within one year.
When is it recommended
Finasteride is mainly recommended for men with androgenetic alopecia, particularly when hair loss is localized at the crown (vertex) or the frontal area and is at an early or moderate stage. Its use is advised when progressive hair thinning is observed, with the aim of slowing disease progression and preserving existing hair.
Treatment should begin after medical evaluation, in order to determine suitability, duration, and dosage based on the patient’s profile.
It is not indicated for use in women, as its hormonal action and alteration of androgen levels may affect the hormonal balance of the female body.
When is it recommended
Finasteride is mainly recommended for men with androgenetic alopecia, particularly when hair loss is localized at the crown (vertex) or the frontal area and is at an early or moderate stage. Its use is advised when progressive hair thinning is observed, with the aim of slowing disease progression and preserving existing hair.
Treatment should begin after medical evaluation, in order to determine suitability, duration, and dosage based on the patient’s profile.
It is not indicated for use in women, as its hormonal action and alteration of androgen levels may affect the hormonal balance of the female body.
Methods of admission
Finasteride can be administered in two main ways, depending on the patient’s needs, side-effect profile, and the intended therapeutic goal:
Oral administration (tablets)
The most common and approved form of administration is oral intake of 1 mg tablets once daily. This dosage inhibits the activity of type II 5-alpha-reductase, leading to a reduction in dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels both in the scalp and in the bloodstream.
Treatment requires continuous daily use, and the first clinical results are usually observed within 4 to 6 months, with maximum therapeutic benefit achieved within 12 months. Effectiveness has been documented in numerous clinical studies, with stabilization or improvement of hair loss reported in up to 80–90% of users.
Topical application (solution or lotion)
Topical finasteride is applied directly to the scalp, usually once daily, at concentrations ranging from 0.25% to 0.5%. Its purpose is the targeted inhibition of DHT in the skin, with minimal systemic absorption, which may reduce the likelihood of adverse effects. The topical form is not widely available, but it has been studied in clinical trials and is used in a large number of cases with very positive results.
Studies indicate that it may offer comparable effectiveness to the oral form, particularly in terms of stabilizing alopecia, with a significantly lower incidence of systemic side effects. It is mainly indicated for individuals who do not tolerate oral therapy or who prefer a more targeted approach.
Methods of admission

Finasteride can be administered in two main ways, depending on the patient’s needs, side-effect profile, and the intended therapeutic goal:
Oral administration (tablets)
The most common and approved form of administration is oral intake of 1 mg tablets once daily. This dosage inhibits the activity of type II 5-alpha-reductase, leading to a reduction in dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels both in the scalp and in the bloodstream.
Treatment requires continuous daily use, and the first clinical results are usually observed within 4 to 6 months, with maximum therapeutic benefit achieved within 12 months. Effectiveness has been documented in numerous clinical studies, with stabilization or improvement of hair loss reported in up to 80–90% of users.
Topical application (solution or lotion)
Topical finasteride is applied directly to the scalp, usually once daily, at concentrations ranging from 0.25% to 0.5%. Its purpose is the targeted inhibition of DHT in the skin, with minimal systemic absorption, which may reduce the likelihood of adverse effects. The topical form is not widely available, but it has been studied in clinical trials and is used in a large number of cases with very positive results.
Studies indicate that it may offer comparable effectiveness to the oral form, particularly in terms of stabilizing alopecia, with a significantly lower incidence of systemic side effects. It is mainly indicated for individuals who do not tolerate oral therapy or who prefer a more targeted approach.
When it should be avoided
Although finasteride is generally well tolerated, there are cases in which its use should be avoided or approached with particular caution, depending on the patient’s medical history and individual needs.
Some of these cases include:
Women
Hypersensitivity
Individuals with known hypersensitivity to finasteride or to any excipient of the formulation.
Reproductive period
Finasteride should preferably be avoided in men who are trying to conceive, as it may temporarily affect sperm quality—an effect that is considered fully reversible after discontinuation of treatment.
Hepatic dysfunction
Individuals with hepatic dysfunction, as finasteride is metabolized in the liver and the risk of adverse effects may be increased.
Drug Interactions
In combination with other anti-androgens without medical supervision, as androgen suppression may be enhanced. Finasteride should be administered under medical guidance in order to assess its suitability for each patient and to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Women
Hypersensitivity
Individuals with known hypersensitivity to finasteride or to any excipient of the formulation.
Reproductive period
Finasteride should preferably be avoided in men who are trying to conceive, as it may temporarily affect sperm quality—an effect that is considered fully reversible after discontinuation of treatment.
Hepatic dysfunction
Individuals with hepatic dysfunction, as finasteride is metabolized in the liver and the risk of adverse effects may be increased.
Drug Interactions
In combination with other anti-androgens without medical supervision, as androgen suppression may be enhanced. Finasteride should be administered under medical guidance in order to assess its suitability for each patient and to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Possible side effects of finasteride
Finasteride is generally well tolerated; however, like any pharmaceutical treatment, it may cause adverse effects in some users.
Most side effects are mild, transient, and resolve after discontinuation of therapy.
The most common side effects are related to sexual function and include:
- decreased libido (sexual desire)
- difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection
- reduced semen volume during ejaculation
Less frequently reported effects include:
- breast tenderness or mild enlargement (gynecomastia)
- mood changes, such as low mood or irritability
- a feeling of fatigue
- mild skin rashes or irritation
Rarely, and mainly after long-term use, changes in liver function tests have been reported.
Effectiveness of finasteride

Effectiveness of finasteride

Finasteride (1 mg taken orally once daily) has been shown to be highly effective in slowing down or even stopping hair loss in men with androgenetic alopecia. In many cases, it also helps enhance hair regrowth.
Combination with other treatments
Minoxidil
Autologous Hair Mesotherapy
Hair Transplantation
FAQs
Contact Form