Female Hair Loss: Causes, Diagnosis & Treatments
What is female hair loss?
Female hair loss is a common and multifactorial disorder characterized by a gradual or sudden decrease in hair density.
Although it does not usually lead to complete loss of hair on the scalp, it significantly affects the appearance and psychology of patients.
The most typical clinical presentation involves diffuse thinning at the top of the head or along the parting line, with preservation of the frontal hairline.
Its etiology includes hormonal fluctuations (e.g., menopause, polycystic ovary syndrome), genetic predisposition, chronic inflammation, nutritional deficiencies, medications, and stress-related factors.
Distinguishing between reversible and non-reversible forms is essential for selecting the appropriate treatment.
Early evaluation by a specialized dermatologist can play a decisive role in stabilizing the condition and restoring hair growth.
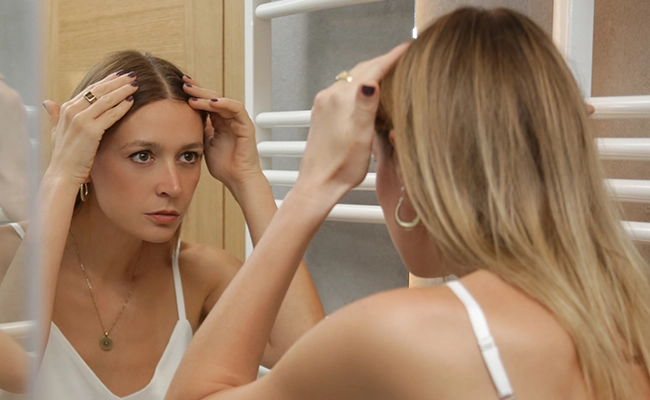


What is female hair loss?
Female hair loss is a common and multifactorial disorder characterized by a gradual or sudden decrease in hair density.
Although it does not usually lead to complete loss of hair on the scalp, it significantly affects the appearance and psychology of patients.
The most typical clinical presentation involves diffuse thinning at the top of the head or along the parting line, with preservation of the frontal hairline.
Its etiology includes hormonal fluctuations (e.g., menopause, polycystic ovary syndrome), genetic predisposition, chronic inflammation, nutritional deficiencies, medications, and stress-related factors.
Distinguishing between reversible and non-reversible forms is essential for selecting the appropriate treatment.
Early evaluation by a specialized dermatologist can play a decisive role in stabilizing the condition and restoring hair growth.

Symptoms of female hair loss
Female hair loss usually does not present with clearly visible bald patches but with milder, gradual signs that often go unnoticed:
- Thinning at the top of the head and along the parting line.Reduced hair density — less volume, especially when tying or styling the hair.
- Increased hair shedding during washing, on the brush, or on the pillow.
- Sensitivity or itching of the scalp in some cases.
- Slow or absent regrowth after normal shedding.
The condition may progressively worsen, especially during periods of intense stress or hormonal changes (menopause, childbirth).Early recognition of the symptoms allows for appropriate diagnostic evaluation and intervention before the hair loss becomes permanent.
Symptoms of female hair loss

Female hair loss usually does not present with clearly visible bald patches but with milder, gradual signs that often go unnoticed:
- Thinning at the top of the head and along the parting line.Reduced hair density — less volume, especially when tying or styling the hair.
- Increased hair shedding during washing, on the brush, or on the pillow.
- Sensitivity or itching of the scalp in some cases.
- Slow or absent regrowth after normal shedding.
The condition may progressively worsen, especially during periods of intense stress or hormonal changes (menopause, childbirth).Early recognition of the symptoms allows for appropriate diagnostic evaluation and intervention before the hair loss becomes permanent.
Causes of female hair loss
Female hair loss may be caused by a wide range of factors—from hormonal and metabolic disorders to genetic and external influences—making accurate diagnosis essential for effective treatment.
The most common causes are:
- Hormonal disorders
Thyroid diseases, polycystic ovary syndrome, menopause, or postpartum hormonal changes. - Heredity & androgenetic alopecia
Genetic predisposition leading to diffuse thinning. - Telogen effluvium
Temporary shedding after stress, illness, surgery, or significant weight loss. - Nutritional deficiencies
Key factors: iron, vitamin D, B-complex vitamins, and zinc. - Medication effects
Oral contraceptives, antithyroid medication, antidepressants, or other drugs associated with hair loss. - Dermatological conditions
Seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, or autoimmune scarring forms. - Poor hair care practices
Frequent heat styling, chemical treatments, hair dyes, or tight hairstyles.
Stages of female hair loss
Female hair loss is usually progressive, with a mild onset and gradual worsening, especially during periods of hormonal changes or intense stress.
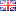
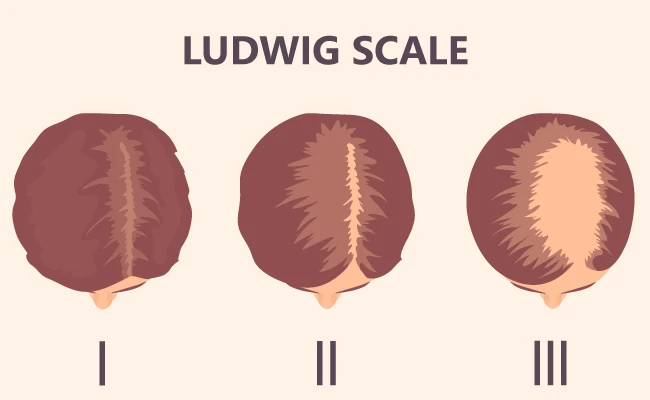
The Ludwig scale is used internationally to describe the severity and distribution of thinning:
Stage I
Mild diffuse thinning at the top of the head with a normal frontal hairline.
Stage II
Visible thinning and widening of the central parting.
Stage III
Extensive thinning at the top of the scalp with significant density reduction.
Stages of female hair loss
Female hair loss is usually progressive, with a mild onset and gradual worsening, especially during periods of hormonal changes or intense stress.
The Ludwig scale is used internationally to describe the severity and distribution of thinning:
Stage I
Mild diffuse thinning at the top of the head with a normal frontal hairline.
Stage II
Visible thinning and widening of the central parting.
Stage III
Extensive thinning at the top of the scalp with significant density reduction.

Diagnosis
The diagnosis of female hair loss requires a systematic and individualized approach to identify the underlying cause and rule out pathological conditions.
The key steps include:
- Medical history and clinical examination
Collection of information regarding the onset, duration, progression, and potential triggering factors. - Trichoscopy (or digital dermoscopy)
A non-invasive examination that allows the study of hair follicle morphology and the distinction between androgenetic, telogen, or scarring alopecia. - Pull test
A simple clinical test used to assess the intensity and type of hair loss. - Laboratory testing
Blood tests to evaluate thyroid function, iron, ferritin, vitamins (e.g., D, B12), and hormones (androgens, prolactin, DHEAS). - Scalp biopsy (in selected cases)
Used to diagnose scarring forms or chronic inflammatory scalp diseases.
Treatment of female hair loss
The therapeutic approach is individualized based on the cause, severity, and progression of the hair loss.
The goal is to stabilize shedding and, where possible, enhance natural hair growth. Some of the available treatment options include:
- Medication
Topical minoxidil (2%).
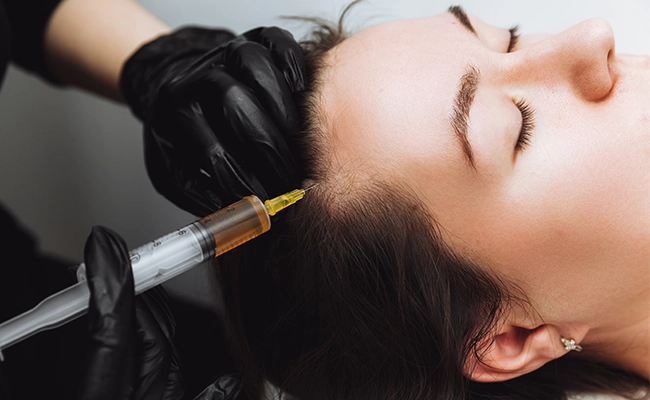
Considered the first-line treatment for female androgenetic alopecia. It is applied topically and enhances vascularization and the hair follicle growth cycle. - Autologous PRP mesotherapy
Autologous mesotherapy using components from the patient’s own blood, which activates the function of the hair follicles. - Heterologous mesotherapies
Local injection of active substances (vitamins, amino acids, peptides) aimed at nourishing and strengthening the scalp. - Hair transplantation
Indicated in stable cases of female androgenetic alopecia with adequate donor supply and localized thinning.Hair transplantation in women is performed with a specialized technique adapted to the pattern and distribution of female alopecia
Treatment of female hair loss

The therapeutic approach is individualized based on the cause, severity, and progression of the hair loss.
The goal is to stabilize shedding and, where possible, enhance natural hair growth. Some of the available treatment options include:
- Medication
Topical minoxidil (2%).
Considered the first-line treatment for female androgenetic alopecia. It is applied topically and enhances vascularization and the hair follicle growth cycle. - Autologous PRP mesotherapy
Autologous mesotherapy using components from the patient’s own blood, which activates the function of the hair follicles. - Heterologous mesotherapies
Local injection of active substances (vitamins, amino acids, peptides) aimed at nourishing and strengthening the scalp. - Hair transplantation
Indicated in stable cases of female androgenetic alopecia with adequate donor supply and localized thinning.Hair transplantation in women is performed with a specialized technique adapted to the pattern and distribution of female alopecia
FAQs
Contact Form