Male Hair Loss: Causes & Treatment
Male hair loss is an extremely common phenomenon that affects the majority of men at some point in their lives. According to research, the first signs appear between the ages of 20–30, with incidence rates exceeding 50% after the age of 50.
The most common form of hair loss in men is androgenetic alopecia, which is associated with the hormone DHT and genetic predisposition. However, hair loss can also be caused by other factors such as stress, nutritional deficiencies, or underlying medical conditions.
The progressive thinning of the scalp often affects men’s psychology, making accurate diagnosis and treatment particularly important.
Early intervention can slow down or even reverse male hair loss, while in more advanced stages there are effective cosmetic and medical solutions, such as various pharmaceutical treatments and hair transplantation.


Male hair loss is an extremely common phenomenon that affects the majority of men at some point in their lives. According to research, the first signs appear between the ages of 20–30, with incidence rates exceeding 50% after the age of 50.
The most common form of hair loss in men is androgenetic alopecia, which is associated with the hormone DHT and genetic predisposition. However, hair loss can also be caused by other factors such as stress, nutritional deficiencies, or underlying medical conditions.
The progressive thinning of the scalp often affects men’s psychology, making accurate diagnosis and treatment particularly important.
Early intervention can slow down or even reverse male hair loss, while in more advanced stages there are effective cosmetic and medical solutions, such as various pharmaceutical treatments and hair transplantation.

Causes of male hair loss
The most common form of male hair loss is androgenetic alopecia.
Its cause is mainly hormonal and genetic, with the combination of these factors leading to gradual thinning and miniaturization of the hair.
Androgenetic alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is caused by the sensitivity of hair follicles to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone. DHT affects the hair follicles on the scalp, primarily in the frontal hairline and the crown area. It also causes their gradual shrinkage and a shortening of the hair growth cycle.
As a result, thinner, shorter, and less pigmented hairs appear, until hair production eventually stops completely.
Sensitivity to DHT is hereditary, so family history plays a decisive role in the onset and severity of male hair loss.
Other aggravating factors
Although DHT is the main cause, there are other factors that may worsen or accelerate hair loss in men:
- Stress and psychological pressure, which affect the hair growth cycle
- Nutritional deficiencies, mainly iron, vitamin D, and zinc
- Thyroid disorders or other hormonal imbalances
- Medications, such as chemotherapy, antiandrogens, or antihypertensives
Although these factors are not directly responsible for androgenetic alopecia, they can intensify it or contribute to additional forms of hair loss.
Causes of male hair loss
The most common form of male hair loss is androgenetic alopecia.
Its cause is mainly hormonal and genetic, with the combination of these factors leading to gradual thinning and miniaturization of the hair.
Androgenetic alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is caused by the sensitivity of hair follicles to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone. DHT affects the hair follicles on the scalp, primarily in the frontal hairline and the crown area. It also causes their gradual shrinkage and a shortening of the hair growth cycle.
As a result, thinner, shorter, and less pigmented hairs appear, until hair production eventually stops completely.
Sensitivity to DHT is hereditary, so family history plays a decisive role in the onset and severity of male hair loss.
Other aggravating factors
Although DHT is the main cause, there are other factors that may worsen or accelerate hair loss in men:
- Stress and psychological pressure, which affect the hair growth cycle
- Nutritional deficiencies, mainly iron, vitamin D, and zinc
- Thyroid disorders or other hormonal imbalances
- Medications, such as chemotherapy, antiandrogens, or antihypertensives
Although these factors are not directly responsible for androgenetic alopecia, they can intensify it or contribute to additional forms of hair loss.

Other aggravating factors
Although DHT is the main cause, there are other factors that may worsen or accelerate hair loss in men:
- Stress and psychological pressure, which affect the hair growth cycle
- Nutritional deficiencies, mainly iron, vitamin D, and zinc
- Thyroid disorders or other hormonal imbalances
- Medications, such as chemotherapy, antiandrogens, or antihypertensives
Although these factors are not directly responsible for androgenetic alopecia, they can intensify it or contribute to additional forms of hair loss.
Symptoms
Male hair loss progresses gradually, following characteristic patterns that allow specialists to recognize and evaluate the condition early. Understanding the symptoms and stages of thinning on the scalp is crucial for choosing the appropriate treatment.
What are the first signs of hair loss in men?
The initial signs may be mild and are often overlooked:
- Thinning at the temples (especially at the corners of the frontal hairline)
- Thinning and loss of density at the crown (vertex)An increased number of hairs on the brush, pillow, or in the shower
- Difficulty styling the hair due to reduced volume
Symptoms
Male hair loss progresses gradually, following characteristic patterns that allow specialists to recognize and evaluate the condition early. Understanding the symptoms and stages of thinning on the scalp is crucial for choosing the appropriate treatment.
What are the first signs of hair loss in men?
The initial signs may be mild and are often overlooked:
- Thinning at the temples (especially at the corners of the frontal hairline)
- Thinning and loss of density at the crown (vertex)An increased number of hairs on the brush, pillow, or in the shower
- Difficulty styling the hair due to reduced volume
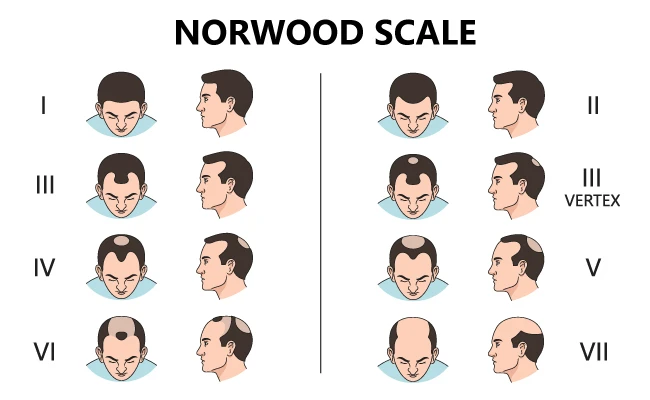
Stages of male hair loss – Norwood-Hamilton scale
The Norwood scale is the most widely known system for classifying androgenetic alopecia in men.
It includes
The Norwood scale is the most widely known system for classifying androgenetic alopecia in men.
It includes 7 stages:
Stage 1: No visible hair loss
Stage 2: Slight recession at the temples
Stage 3: Visible recession of the frontal hairline
Stage 4: Further hair loss at the crown and temples
Stage 5: The thinning areas begin to merge
Stage 6: Near-complete merging of frontal and crown thinning
Stage 7: Extensive hair loss – only the hair on the sides and back remains
Stages of male hair loss – Norwood-Hamilton scale
The Norwood scale is the most widely known system for classifying androgenetic alopecia in men.
It includes
The Norwood scale is the most widely known system for classifying androgenetic alopecia in men.
It includes 7 stages:
Stage 1: No visible hair loss
Stage 2: Slight recession at the temples
Stage 3: Visible recession of the frontal hairline
Stage 4: Further hair loss at the crown and temples
Stage 5: The thinning areas begin to merge
Stage 6: Near-complete merging of frontal and crown thinning
Stage 7: Extensive hair loss – only the hair on the sides and back remains

How is the diagnosis performed?
Male hair loss is treated according to the stage of alopecia and the specific needs of each patient.
Clinical examination
The doctor examines the scalp for signs of thinning, the pattern of hair loss, and any irritations. Family history and the rate at which the hair is shedding are also assessed.
Trichoscopy
Using a specialized microscope, the hairs and follicles are observed for miniaturized hairs, signs of weakness, or possible inflammation.
Trichogram
A measurement is taken of the ratio between hairs in the growth phase and those in the shedding phase, in order to assess the health of the hair follicles.
Blood tests (if needed)
In certain cases of male hair loss, hormone testing (e.g., testosterone, DHT) and vitamin/iron testing (iron, ferritin) may be recommended to identify possible deficiencies or hormonal imbalances.
Early diagnosis is the key to effectively addressing male hair loss. Book a free diagnostic appointment with our specialists today and find out which solution is right for you!
Treatment of male hair loss
Male hair loss is treated according to the stage of alopecia and the individual needs of each patient. For this reason, an evaluation by a specialist is essential in order to identify the causes and type of hair loss.
The available options are divided into two main categories:
Non-invasive treatments
These include treatments such as autologous hair mesotherapy, which strengthens the hair follicles using the patient’s own blood. Minoxidil, applied topically, also helps maintain and enhance existing hair growth.
Surgical solutions
Hair transplantation, using techniques such as FUE or FUT, offers a permanent solution in areas of thinning, restoring the natural appearance of the hair.
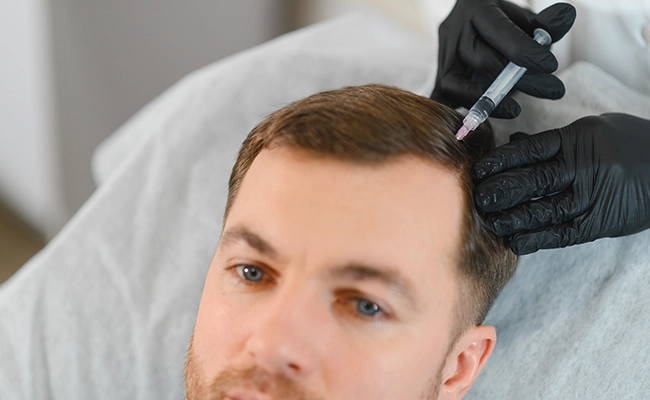

Treatment of male hair loss

Male hair loss is treated according to the stage of alopecia and the individual needs of each patient. For this reason, an evaluation by a specialist is essential in order to identify the causes and type of hair loss.
The available options are divided into two main categories:
Non-invasive treatments
These include treatments such as autologous hair mesotherapy, which strengthens the hair follicles using the patient’s own blood. Minoxidil, applied topically, also helps maintain and enhance existing hair growth.
Surgical solutions
Hair transplantation, using techniques such as FUE or FUT, offers a permanent solution in areas of thinning, restoring the natural appearance of the hair.
FAQs
Contact Form