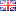
Hair Loss: Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
Hair loss is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, regardless of age or gender.
Beyond its aesthetic impact, hair loss can significantly influence a person’s psychology, confidence, and overall quality of life. Many individuals experience stress or insecurity when they notice their hair thinning or falling out. Losing 50–100 hairs per day is considered normal.
However, when hair shedding increases and is accompanied by thinning or bald patches, it may indicate pathological hair loss. Hair loss can be triggered by multiple factors—sometimes combined—including genetics, hormonal imbalances, stress, nutritional deficiencies, and even certain medications.
Correct diagnosis is the first and most important step in managing hair loss. With proper assessment and modern treatments, most cases can be effectively addressed.


Hair loss is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, regardless of age or gender.
Beyond its aesthetic impact, hair loss can significantly influence a person’s psychology, confidence, and overall quality of life. Many individuals experience stress or insecurity when they notice their hair thinning or falling out. Losing 50–100 hairs per day is considered normal.
However, when hair shedding increases and is accompanied by thinning or bald patches, it may indicate pathological hair loss. Hair loss can be triggered by multiple factors—sometimes combined—including genetics, hormonal imbalances, stress, nutritional deficiencies, and even certain medications.
Correct diagnosis is the first and most important step in managing hair loss. With proper assessment and modern treatments, most cases can be effectively addressed.
General information
Hair loss refers to the gradual or sudden shedding of hair from the scalp or other areas of the body. While daily hair shedding is normal, excessive or persistent loss accompanied by reduced hair density is considered abnormal and requires evaluation.
Who does hair loss affect?
Hair loss affects both men and women: According to studies, 50% of men experience some degree of hair loss by age 50. Approximately 55% of women experience noticeable hair thinning during their lifetime, often after pregnancy or during menopause.
Temporary vs permanent hair loss
Temporary hair loss can be caused by factors such as stress, illness, nutritional deficiencies, infection, or hormonal shifts. Hair typically grows back once the cause is resolved.
Permanent hair loss usually hereditary (androgenetic alopecia) or related to scarring of the follicles. This form progresses gradually and requires early treatment to slow down the process.
Main causes of hair loss
Hair loss can result from genetic, hormonal, inflammatory, psychological, and environmental factors. Identifying the root cause is crucial for choosing the right treatment.
The main causes seem to be:
Heredity
Hereditary factors are the most common cause of hair loss and can be inherited from either parent. This type is called androgenetic alopecia, and it usually appears gradually with a predictable progression.
In men, it causes receding of the frontal hairline and localized thinning.
In women, it leads to hair shaft thinning and diffuse thinning along the top of the scalp.
Hormonic changes and medical conditions
A variety of conditions can cause permanent or temporary hair loss. These include hormonal changes due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, and thyroid disorders.
As for medical conditions, they include:
- Alopecia areata, which is related to the immune system and causes patchy hair loss
- various scalp infections
- trichotillomania.
Medication and supplements
Hair loss can be a side effect of certain medications, such as those used for:
- cancer
- arthritis
- depression
- heart conditions
- supplements used for weight control and muscle mass enhancement.
Stress
Several people experience general hair thinning several months after an emotional shock. This type of hair loss is usually temporary, but an evaluation by a specialist is always recommended.
Harmful hair care habits
Excessive chemical treatments, such as frequent bleaching and low-quality dyes, lead to hair shaft thinning, loss of volume, and eventually scalp thinning.
Similarly, constant hairstyles that pull the hair tightly or improper application of extensions can cause traction alopecia.
Environmental factors
The health of the scalp and hair follicles can be negatively affected by environmental factors such as:
- air pollution
- ultraviolet (UV) radiation
- exposure to toxic substances
Long-term or repeated exposure to such conditions can contribute to premature hair damage and the gradual onset of hair loss.
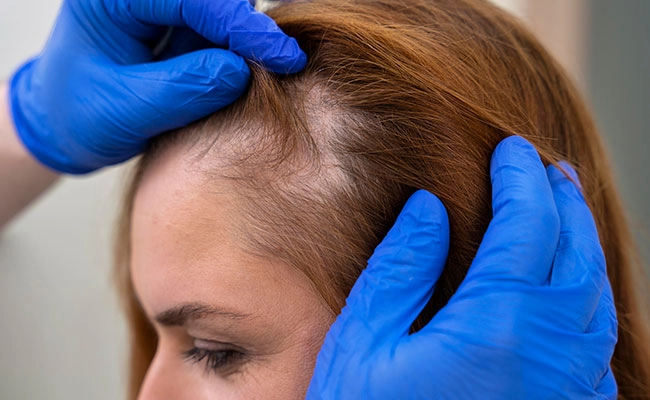
The life cycle of hair
From their emergence to their shedding, hairs go through 4 stages of development, which are:
The life cycle of hair
From their emergence to their shedding, hairs go through 4 stages of development, which are:
Anagen phase (Hair growth stage)
The anagen phase is the longest stage of the hair growth cycle, lasting 2 to 8 years for scalp hair. During this phase, hair actively grows, and about 85% to 90% of scalp hairs are in the anagen phase at any given time.
Catagen phase (Transitional hair stage)
The catagen phase is a short transitional stage that lasts around 2 weeks. Hair follicles shrink and hair growth slows down. Only 1% to 3% of scalp hairs are in this phase. Telogen Phase (Resting Hair Stage) The telogen phase lasts 2 to 3 months and is a resting stage for hair follicles. Hair growth temporarily stops, but hair usually remains in the follicle. Around 9% of scalp hairs are in the telogen phase.
Exogen phase (Hair shedding stage)
The exogen phase is the shedding stage of the hair cycle, extending the telogen phase for several months. During exogen, old hairs fall out while new hairs begin to grow, keeping the hair cycle continuous and healthy.
Anagen phase (Hair growth stage)
The anagen phase is the longest stage of the hair growth cycle, lasting 2 to 8 years for scalp hair. During this phase, hair actively grows, and about 85% to 90% of scalp hairs are in the anagen phase at any given time.
Catagen phase (Transitional hair stage)
The catagen phase is a short transitional stage that lasts around 2 weeks. Hair follicles shrink and hair growth slows down. Only 1% to 3% of scalp hairs are in this phase. Telogen Phase (Resting Hair Stage) The telogen phase lasts 2 to 3 months and is a resting stage for hair follicles. Hair growth temporarily stops, but hair usually remains in the follicle. Around 9% of scalp hairs are in the telogen phase.
Exogen phase (Hair shedding stage)
The exogen phase is the shedding stage of the hair cycle, extending the telogen phase for several months. During exogen, old hairs fall out while new hairs begin to grow, keeping the hair cycle continuous and healthy.

Types of hair loss (Alopecia forms)
Hair loss can be temporary or permanent, depending on its underlying cause. Some types of alopecia are reversible and can be treated with proper therapy, while others may lead to irreversible hair loss. The most common types of hair loss include:
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male & female pattern baldness)
Androgenetic alopecia is the most common form of hair loss, primarily caused by genetic predisposition and the sensitivity of hair follicles to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It is characterized by gradual thinning of hair, typically in specific areas of the scalp, and affects both men and women.
Diffuse Alopecia
Diffuse alopecia is marked by uniform and sudden hair thinning across the entire scalp without creating specific bald spots. It is usually linked to temporary disruptions in the hair growth cycle, caused by physical or emotional stress, hormonal changes, infections, or nutritional deficiencies.
Cicatricial (Scarring) Alopecia
Cicatricial alopecia is a permanent type of hair loss resulting from destruction of hair follicles, often due to inflammation or trauma to the scalp. As follicles are replaced by scar tissue, hair loss becomes irreversible. Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent further damage.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is a sudden, localized hair loss that appears as small, round, or oval bald patches on the scalp or other parts of the body. Its progression is often unpredictable and is usually associated with autoimmune conditions.
Universal Alopecia (Alopecia Universalis)
Universal alopecia is an extensive form of alopecia areata, leading to complete hair loss on the scalp and body. It differs from alopecia areata, which causes specific bald spots, and total alopecia (alopecia totalis), which causes complete scalp hair loss only.
Hair loss symptoms
The symptoms of hair loss vary depending on the type and underlying cause. In most cases, hair loss presents with one or more of the following signs:
Hair thinning
This is the most common symptom of hair loss. It often develops gradually, particularly on the top of the head or temples in men, and as diffuse thinning in women.
Sudden hair shedding
Sudden hair loss is often observed after intense stress, illness, childbirth, or surgery. Hair may fall out easily during washing or brushing.
Bald patches
Circular or oval hairless areas, such as those seen in alopecia areata, typically appear without pain or irritation.
Scalp irritation
In inflammatory or scarring forms of alopecia, symptoms may include pain, itching, redness, or flaking.
Hair shaft thinning
Hair strands may become weaker and finer over time, making the hair appear less dense and more prone to breakage.
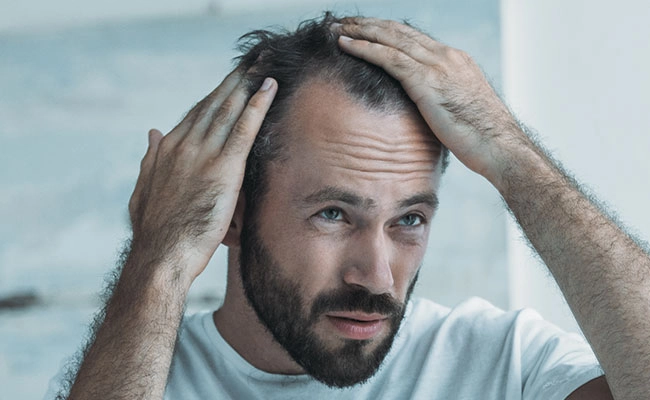
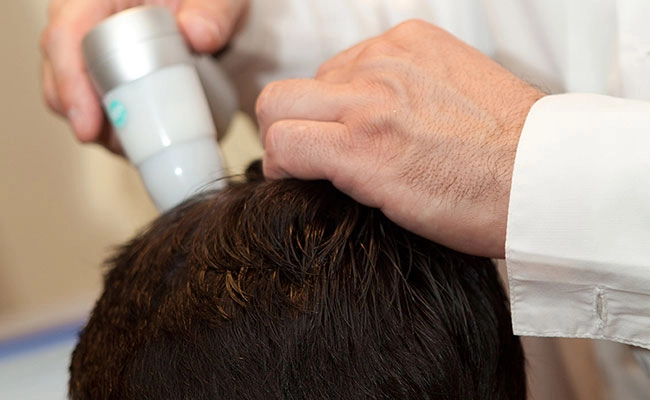
Hair loss diagnosis
Effective hair loss treatment begins with identifying the underlying cause. The diagnosis of hair loss starts with a thorough clinical examination and detailed medical history to detect potential factors such as genetics, stress, and hormonal changes.
Common diagnostic methods include dermatoscopy and blood tests to evaluate the health of the scalp and hair follicles.
In some cases, a scalp biopsy may be necessary for a more precise diagnosis, especially when there are signs of scarring or inflammatory alopecia.
Hair loss diagnosis

Effective hair loss treatment begins with identifying the underlying cause. The diagnosis of hair loss starts with a thorough clinical examination and detailed medical history to detect potential factors such as genetics, stress, and hormonal changes.
Common diagnostic methods include dermatoscopy and blood tests to evaluate the health of the scalp and hair follicles.
In some cases, a scalp biopsy may be necessary for a more precise diagnosis, especially when there are signs of scarring or inflammatory alopecia.
FAQs
Contact Form