Dutasteride for Hair Loss
Dutasteride is a highly effective medication for combating hair loss. It can be administered either orally or through topical application.
It is used to treat androgenetic alopecia, as it functions as an anti–hair loss therapy. As a result, the popularity of this treatment option has increased significantly in recent years.
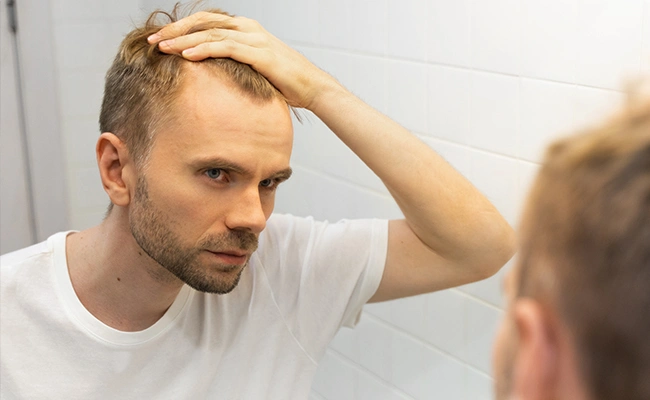

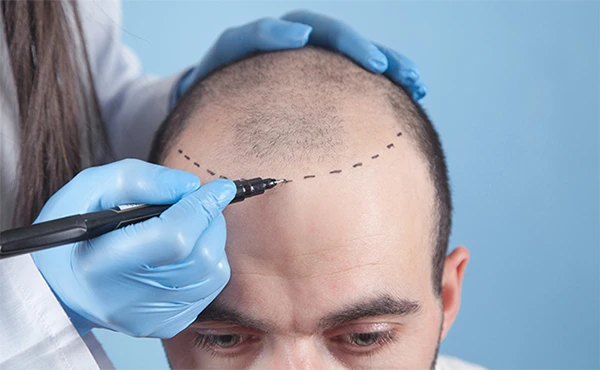
What is dutasteride
How does dutasteride work against hair loss
Topical dutasteride
What is the dosage
Dutasteride is usually prescribed at a dose of 0.5 mg per day when taken in oral tablet form. It is taken once daily. In some cases, lower doses or reduced dosing frequency may be used, achieving very good results while limiting side effects.
In the case of topical dutasteride, the dosage and frequency of application are determined after medical evaluation and depend on the concentration of the formulation. Typically, concentrations range from 0.1% to 0.5%; as the concentration increases, systemic absorption also increases.
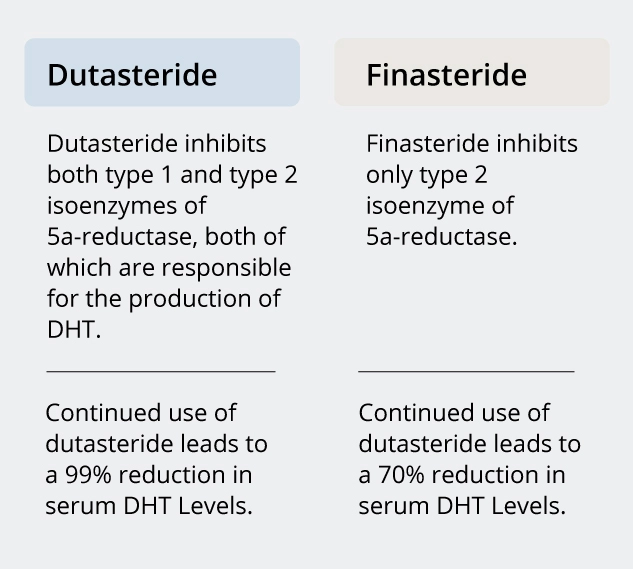
Dutasteride vs Finasteride
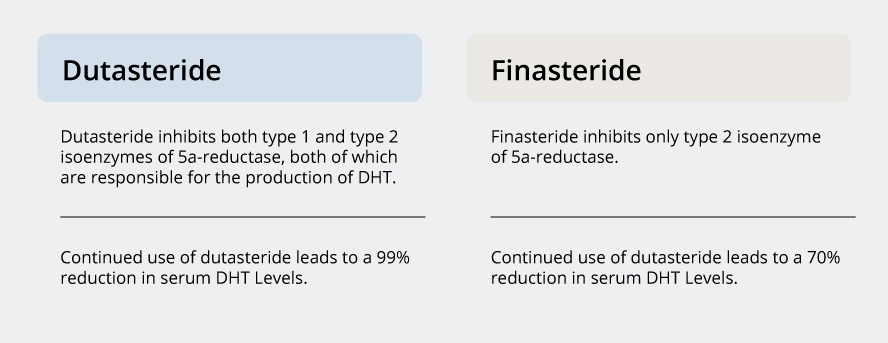
Dutasteride vs Finasteride
Dutasteride vs Minoxidil
Dutasteride targets the hormonal cause of hair loss by blocking the action of DHT. In contrast, minoxidil is a pharmacological treatment that works by improving blood circulation to the hair follicles.
In general, dutasteride is considered a more effective treatment than topical minoxidil in slowing the progression of androgenetic alopecia and promoting hair regrowth.

Dutasteride vs Minoxidil
Dutasteride targets the hormonal cause of hair loss by blocking the action of DHT. In contrast, minoxidil is a pharmacological treatment that works by improving blood circulation to the hair follicles.
In general, dutasteride is considered a more effective treatment than topical minoxidil in slowing the progression of androgenetic alopecia and promoting hair regrowth.

Side effects
Dutasteride is generally considered a safe and well-tolerated medication; however, like any pharmaceutical treatment, it may cause side effects.
With oral administration, the most common side effects are mainly sexual in nature and include:
- decreased libido (sexual desire)
- erectile dysfunction
- ejaculatory disorders
More rarely, the following may occur:
- gynecomastia (breast enlargement in men)
- testicular pain or tenderness
- allergic reactions
- mood changes or depressive symptoms
Are you looking for a solution to hair loss?
Proper information on effective hair loss treatment is the first step before any therapy.
Contact our clinics for a personalized diagnosis.