Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
What is DHT
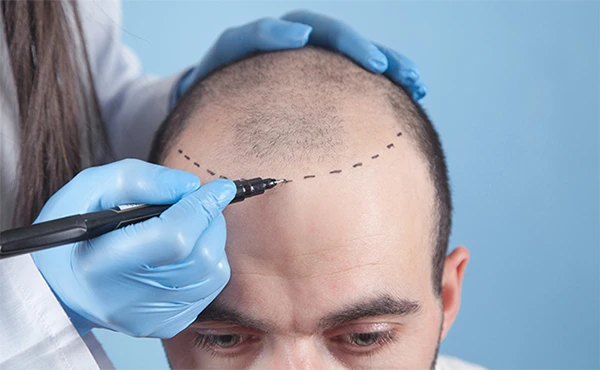
DHT is a derivative of testosterone. This hormone is responsible for the development of male characteristics, such as muscle formation, facial and body hair growth, and voice deepening.
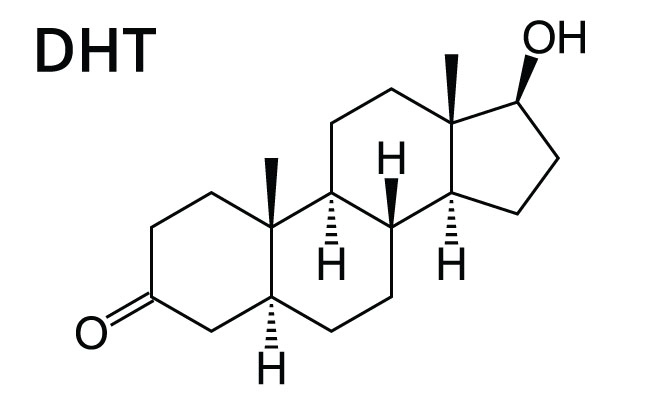
It is produced through an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into DHT. DHT is present in both men and women; however, its levels are higher in men.
How DHT causes hair loss
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is the primary cause of androgenetic alopecia. It affects the hair follicles by causing them to shrink, resulting in hair that grows thinner, weaker, and eventually falls out.
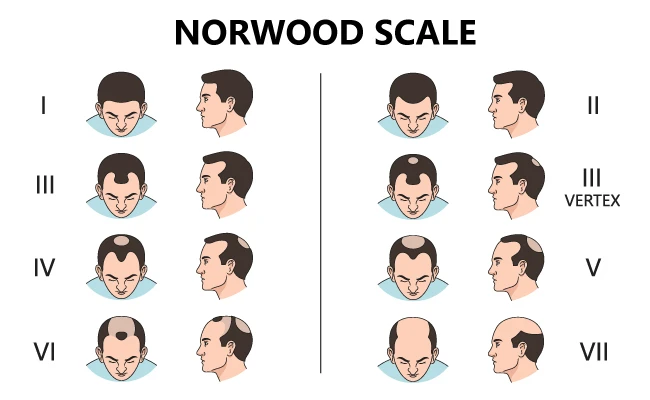
In men, hair loss caused by androgenetic alopecia follows a specific pattern, which is accurately described by the Norwood scale. It usually begins with recession of the frontal hairline and is followed by thinning at the crown of the scalp.
In cases of advanced male hair loss and over time, these areas may merge. As a result, hair remains only at the back and sides of the scalp, forming a “rim” or horseshoe-shaped pattern.
How it’s treated
There are effective options known as DHT inhibitors, which aim either to reduce DHT levels or to block its action on hair follicles. In this way, the progression of hair loss can be slowed and, in some cases, hair regrowth may be achieved.
Finasteride
Finasteride is one of the most widely used substances for combating DHT. It works by inhibiting the 5-alpha reductase enzyme, thereby reducing the conversion of testosterone into DHT.
Dutasteride
Dutasteride is a more potent 5-alpha reductase inhibitor, as it acts on multiple types of this enzyme. As a result, it leads to a more significant reduction in DHT levels.
Conclusion
DHT (dihydrotestosterone) is the primary hormonal factor associated with the development of hair loss; however, it does not affect everyone in the same way. With proper diagnosis and individualized treatment, the progression of hair loss can be slowed or effectively controlled.
Are you looking for a solution to hair loss?
Proper information on effective hair loss treatment is the first step before any therapy.
Contact our clinics for a personalized diagnosis.